In recent years, nearly 70% of manufacturers have used laser cutting for accurate and efficient production. Industrial cutting machines use a concentrated laser beam to engrave materials accurately. Sectors like automotive, aerospace, and fashion need it. Due to its accuracy, laser is ideal for large manufacturing and customized design, including but not limited to modern laser cut gate design and laser cut balcony railing.
Meanwhile, this article will cover a basic overview of what is laser cutting, how it works, its history, materials used, applications, advantages, and disadvantages.
What is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting is a precise manufacturing process in which a high-powered laser beam is directed through optics to cut, engrave, or etch materials with tolerances within microns.
Types of CNC Laser Cutting Machines
- CO2 Laser Cutting Machines.
- Fiber Laser Cutting Machines.
- Nd (Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) Laser Cutting Machines.
- UV Laser Cutting Machines.
- Green Laser Cutting Machines.
- Mini Laser Cutting Machines.
Key Components
Laser cutting metal machines have a laser source, a cutting bed, and a CNC-controlled movement system. The laser source generates a high-energy beam to cut. The cutting bed is where the material is placed for movement along axes to position the material under the laser. The optics, including lenses and mirrors, direct the laser beam onto the material. Nitrogen or oxygen may enhance cutting efficiency while expelling molten material or preventing oxidation. A control system manages the machine’s operations and translates design files into cutting paths.
How Does Laser Cutting Work?
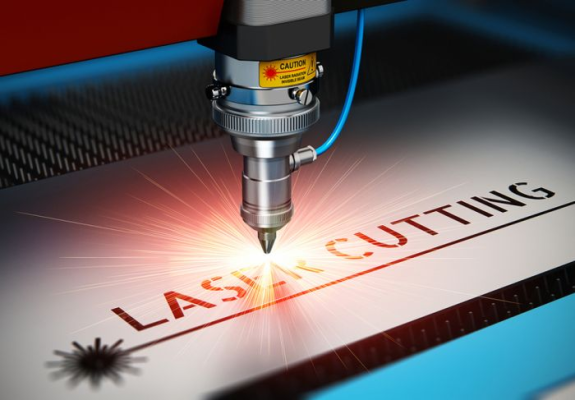

Basic Process Steps Involved
- Generation of the laser beam through electrical/optical pumping.
- Beam delivery via optical components (mirrors/optical fibers).
- Focusing the beam to a precise spot on the material’s surface.
- Initiating the cut while piercing the material.
- Moving the beam along the cutting path.
- Adjusting cutting speed and power for material thickness.
- Removing molten material (kerf) via assist gas.
- Monitoring cut quality with a CNC metal laser cutting machine.
Control Systems
CNC systems guide the cutting laser with precision in complex geometries and high-tolerance applications. They convert CAD models into machine instructions and control the laser’s movement along the X, Y, and Z axes. The CNC also adjusts the beam power, focus height, and gas pressure for ideal cutting conditions. For instance, in a laser metal cutting machine, the CNC Machining compensates for material thickness variations to lower the jeopardy of defects.
History of Laser Cutting
The first production laser machine drilled diamond die holes in 1965. Western Electric Engineering Research Center produced this equipment. After that, the British invented laser-assisted oxygen jet metal cutting in 1967. In the early 1970s, the cutting technique was developed for titanium in aerospace applications. On the other hand, CO2 lasers were also used to cut fabrics since they were too weak to overcome metals’ thermal conductivity.
Materials Used in Laser Cutting
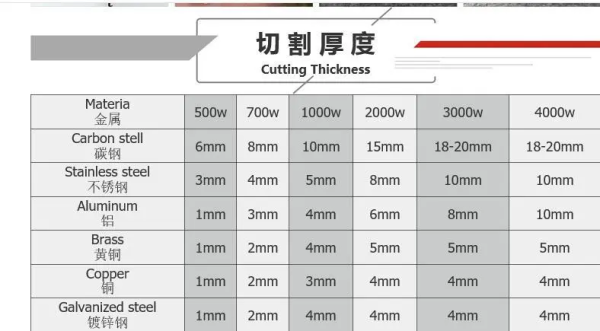
Metals
Laser cutting is used for steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. Brass laser cut parts are standard in industries needing precise, tricky designs. Metals’ reflectivity in laser engraving machine gold silver and cutting processes requires special laser settings to avert beam reflection damage.
Acrylic
Acrylic is preferred for laser cutting due to its clean, polished edges. A specialized acrylic laser machine helps avoid overheating and guarantee smooth cuts. Laser machine for cutting acrylic should have appropriate ventilation for fumes, which might be toxic if not controlled.
Wood
Wood is multipurpose for laser cutting and offers crisp cuts with negligible scorching. Yet, wood density and resin content can affect the quality. Different woods, including MDF and plywood, behave differently under the laser and need tunings in power settings to avoid burning.
Plastics
ABS, polycarbonate, and polyethylene respond well to cutting but have challenges. Some emit harmful fumes when cut. It requires vigilant selection of laser type and ventilation systems. Thin plastic sheets can melt or warp if not cut with accurate, measured laser power.
Composites
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers might be challenging due to their layered structure. The laser must be potent enough to cut through multiple layers with edge quality. Controlling heat-affected zones helps inhibit delamination or impairment of the composite material.
Applications of Laser Cutting
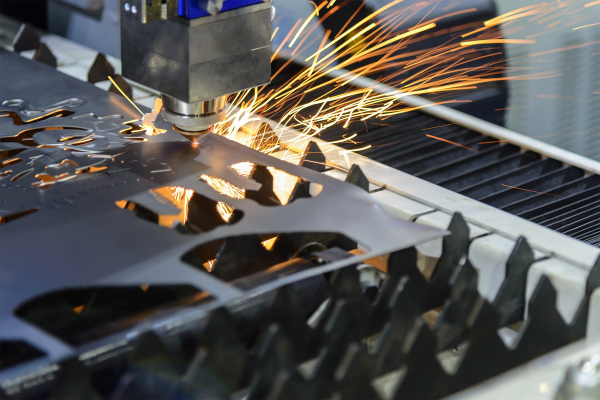

Precision Fabrication
Laser cutting can offer precision fabrication with iron sheets. An iron sheet laser machine can realize designs with slight heat distortion. It suits the aerospace and automotive sectors.
Custom Acrylic Designs
When working with acrylic, laser cutting gives incomparable detail. For instance, acrylic sheets for cutting allow spotless, polished edges without secondary processing. It helps create custom signage, displays, and sophisticated art pieces.
Efficient Tube Processing
A tube laser machine is indispensable for tubular materials. It cuts complex holes and slots on cylindrical surfaces. It can benefit the construction and heavy machinery sectors.
Industrial Tree Cutting
Tree laser cutting machines focus on organic materials in industrial forestry. They precisely process tree trunks for efficient and dependable cuts that decrease material surplus. The technology may also be applied in woodworking and furniture making.
Versatile Tube Cutting
A laser tube cutting machine helps cut tube shapes, including round, square, and rectangular. It gives unfailing quality in cuts for mass production in manufacturing and architecture. Plus, cutting multifaceted angles disregards multiple processing steps.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is precise, efficient, and agile for industrial applications. Still, it’s not without drawbacks when considering laser cutting machines prices. On the upside, laser cutting acrylic can attain convoluted designs with tolerances as tight as ±0.0005 inches for components in aerospace and medical device manufacturing. Challenging materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium, can be processed with negligible thermal distortion due to the focused laser beam. It disregards secondary finishing processes to save time and cost.
Additionally, with appropriate settings, the same machine can switch between cutting, engraving, and drilling tasks for flexibility. However, the process can be sluggish when cutting thicker materials. The power requirement increases exponentially with thickness and demands more expensive high-power lasers. Also, reflective copper or brass can damage the machine’s optics for increased upkeep costs and idle time. Although minimal, the heat-affected zone can still alter the material properties for applications requiring rigid material integrity.
Laser cutting machines prices can be influenced by power output, machine bed size, and automated material handling. E.g., high-end fiber lasers with multi-kilowatt power ratings and automation can reach $600,000. Lower-power systems for small-scale production or prototyping might cost around $20,000. Yet, the preliminary investment and working costs can be prohibitive for small manufacturers when compared to traditional waterjet or plasma cutting. Further, the learning curve of optimizing focal length, pulse duration, and cutting speed can be steep. Looking for quality laser machine cutting services? Contact MXY Machining and see the magic.
Conclusion
Laser cutting machines are an impressive example of how technology is driving change and benefiting different industries. The many advantages of this innovational technology have revolutionized the manufacturing industry by increasing speed, productivity, ease of automation, and the ability to produce highly customized products with unparalleled precision. The benefits of laser cutting go beyond the manufacturing sector and have an exceptional environmental impact, reducing waste and energy consumption. New materials are being discovered, and there is no doubt that the future is bright for laser machines. Industries that invest in this technology have tremendous opportunities for further growth and success.







