Die casting is a common manufacturing technique that uses molds to create various metal parts by applying high pressure to force molten metal into the mold. This method is particularly famed for the possibility of producing multiple forms and shapes with high surface quality and small tolerances. Due to their specific characteristics, aluminum, zinc, magnesium, and copper are some of the most frequently used materials in die casting.
The process is very efficient, which makes it suitable for use in large-scale production, especially in car manufacturing, aircraft manufacturing, electronics, and manufacturing of consumer products. The ability to produce accurate, fast, and complex designs makes die casting the most suitable method for creating strong, detailed metal components. Companies like Mxy machining work with die casting services that guarantee that the parts produced are of high quality. For automotive engine parts or electronics cases, die casting remains a vital process in the contemporary world.
Die Casting and Its Applications in Manufacturing
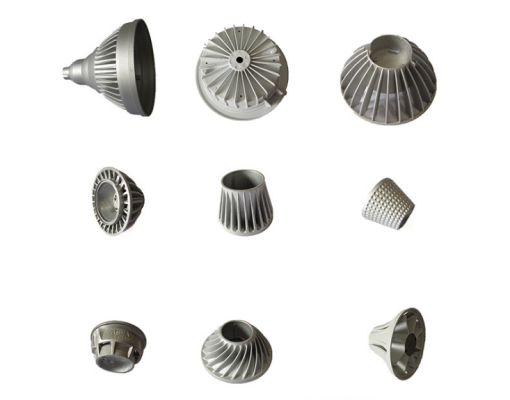

Die casting is one of the most critical manufacturing procedures for producing metal parts. This process involves pouring melted metal into a mold and using high pressure to shape it. This technique is famous for creating parts with high surface finish and accuracy. Of all the die-casting materials, aluminum and zinc are most commonly used because of their light and durable natures. Automotive, aerospace industries, and consumer products industries use die-cast parts in their production. For instance, die-cast car models, including die-cast car 1:24 and die-cast car 1:64, are prized by collectors due to their well-designed detail.
This process is carried out using die casting machines such as the hot chamber die casting machines and the cold chamber die casting machines. These machines help manufacture parts such as aluminum die-casting mold and zinc alloy die-casting parts. Apart from cookware, die-cast toy cars and custom die-cast aluminum products are some of the many uses of die-casting. The versatility in creating shapes makes the process a critical component in today’s manufacturing industries. The application of die-casting is not limited only to the production of bike models; it also includes engraved die-cast gold and silver key chains, showing how die-casting is becoming more diverse as it moves to different industries.
How Does Die Casting Work? Step by Step Die Casting processes
Die-casting is an exciting and effective technique for creating metal parts with high accuracy. It involves several important processes, starting with the creation of a strong mold and then the injection of molten metal into the final product. This is useful in producing intricate geometries with high-dimensional accuracies, making them suitable for industry use.
- Preparation of the Mold: A strong steel tool called a die is made to produce the part with exact detail.
- Melting the Metal: The chosen metal (aluminum, zinc, magnesium, or copper) is heated in a furnace until it turns into a liquid.
- Injecting Molten Metal: The molten metal is forced into the mold cavity at high pressure to fill all the details.
- Cooling and Solidification: The metal cools and forms a mold in its shape. The purpose of this step is to enhance the required accuracy in the process of cooking.
- Ejecting the Part: After the mold is filled and the material has solidified, the mold is opened, and the newly created part is removed with ejector pins.
- Trimming and Finishing: The unwanted material is removed, and further operations, such as polishing or machining, may be applied to achieve the desired surface finish.
Thus, die casting effectively creates intricate and accurate metal components with fine surface quality for use in numerous industries.
Brief History of die casting
Die-casting began in the middle of the nineteenth century when, in 1838, Eliphalet Remington, an American inventor, created the first die-casting machine. Initially, it was used to develop the lead-type characters used in printing presses and quickly adapted itself when the Industrial Revolution came into the picture. Modern die-casting machines invented in 1907 were highly efficient for high production rates, revolutionizing manufacturing.
After the Second World War, there were remarkable developments, and aluminum and zinc gained popularity as they were light and strong. Die casting finds application in making car models, auto parts, aircraft components, and toys, among other products, through the use of die-cast aluminum parts. Computer-aided design and manufacture have added more value to die casting, enabling better and faster die casting for items used in homes, such as die-cast cookware sets or special die-cast aluminum parts.
Materials Commonly Used in Die Casting Process
Die casting process uses several metals, and all of them are used depending on their characteristics and, therefore, their versatility. Here are the most commonly used materials in die casting: Below are the popular materials that are used in die casting:
Aluminum:
Aluminum:
- Lightweight and Strong: Aluminum is preferred because of its strength-to-weight ratio.
- Corrosion-resistant: It can automatically form a passive oxide layer, which helps increase the strength of the material.
- High Thermal Conductivity: Ideal for devices housed in electronic cabinets and car parts.
Zinc:
- High Ductility: It can be formed into any desired design with thin walls, as zinc proves.
- Strong and Tough: It has good mechanical characteristics and is very resistive.
- Cost-Effective: Zinc is relatively inexpensive and can be used in large-scale programs.
Magnesium:
- Ultra-Lightweight: It is a structural metal that is lighter than all the other metals, reducing the weight of the parts.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: It provides good strength as far as the shoe is concerned without weight addition.
- Good Machinability: A machine that produces various parts that are very accurate and have close tolerances is easy to use.
Copper:
- Excellent Conductivity: Copper is used in an environment where the conductivity of both electricity and heat is desirable.
- Corrosion Resistance: Copper and its alloys are also immune to corrosion; this implies they can be used in harsh environments.
- High Strength: Provides perfect and durable parts.
These materials, including aluminum, zinc, magnesium, and copper, are chosen based on the specific requirements of the parts being produced, such as strength, weight, and resistance to corrosion. Their unique properties make die casting a crucial process in industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to electronics and consumer goods.
Uses of Die Casting in Different Sectors
Die casting is a vital manufacturing process in various industries since it yields complex, high-precision components in the shortest possible time. Die casting is critical in the automotive sector in manufacturing lightweight and strong products such as die-cast car models, aluminum die-casting parts, and die-cast car 1:24 replicas. These parts benefit from aluminum and zinc die casting, which have high strength and excellent surface finishes.
In aerospace, die casting is used to manufacture parts such as brackets, housings, and landing gears, among others, because accuracy is very important. Another industry that widely uses die casting is the electronics industry, which produces enclosures, connectors, and heat sinks.
Die casting also creates die-cast cookware, toy cars, and custom die-cast aluminum products in the consumer goods category. Products like die-cast cookware sets, bike models, and engraved die-cast gold and silver key chains are usually die-cast to ensure they are tough and well engraved. It is also applied in producing die-cast drum hoops, die-cast 1:18 scale cars, and classic car models since it produces complex designs and fine surface finishes.
Industrial die-casting uses include
- creating die-cast aluminum components for machines,
- junction boxes of explosion-proof aluminum die-casting used in safety equipment and
- die-casting molds used in tool production.
Hot chamber die-casting machines and cold chamber die-casting machines are used depending on the metal being used and the properties required in the final product. Die-casting machines and aluminum die-casting machines are vital in ensuring that the parts being produced are efficient.
Due to its flexibility and efficiency, die casting is widely used in the automotive, aerospace, electronics, consumer durables, and industrial machinery industries. It always supplies high-value, intricate components that contribute to advancements and effectiveness in those industries.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Die Casting
Advantages of Die Casting
Die casting process offers numerous advantages that make it a preferred manufacturing method across multiple sectors:
- High Precision and Complexity: High complexity and intricacy of the parts that can be manufactured and good dimensional control. This precision is very important in making die-cast car models, bike parts, and die-cast toy cars since the designs have to be well-detailed.
- High-Speed Production: Die casting can also be done at a very high speed. This is why die casting is applicable in industries with a high production of products such as die-cast utensils, cookware sets, and aluminum die-cast products.
- Superior Surface Finish and Strength: Die-casting materials like aluminum and zinc offer strong and long-lasting parts, whether a 1:18-scale car model or an aluminum die-casting mold.
- Efficiency: The process is very effective regarding material utilization, and almost no additional processing is required. This efficiency is useful for creating special die-cast aluminum and zinc alloy die-casting products.
Disadvantages of die-casting
Despite its many benefits, die casting also has some disadvantages:
- High Initial Setup Cost:Die-casting molds and machines are expensive and, therefore, not economical for low production runs because of the initial cost of acquiring them.
- Expensive Design Changes: The molds are complex, and thus, modifications to the part designs are costly and time-consuming.
- Material Limitations: The process is usually restricted to metals with low melting points, such as aluminum and zinc alloys, which, therefore, may not be very useful in certain fields.
- Porosity Issues: Porosity is one of the major problems observed in die-cast parts, which can become a problem in the final product. This is a problem when creating parts that need to be very strong and durable, such as parts for aircraft or automobiles.
However, as has been seen, die casting’s benefits, such as precision, speed, and the possibility of forming intricate shapes, overshadow its demerits, making it a crucial technique in the current world.
CTA

Die casting is an essential process in modern manufacturing, offering high precision, efficiency, and versatility for producing complex metal parts. Companies like MXY Machining excel in providing top-notch die casting services, utilizing advanced technologies and materials such as aluminum, zinc, magnesium, and copper. Their commitment to quality and innovation ensures that industries ranging from automotive to electronics benefit from reliable and high-performance components.







