Explore how 3D printing in automotive industry with complex part designs, rapid prototyping, and on-demand production. Discover the impact on lightweight materials, electric vehicles, and future manufacturing trends. Learn how additive manufacturing is transforming vehicle design, performance, and sustainability.
Innovative Applications of 3D Printing in Automotive Industry

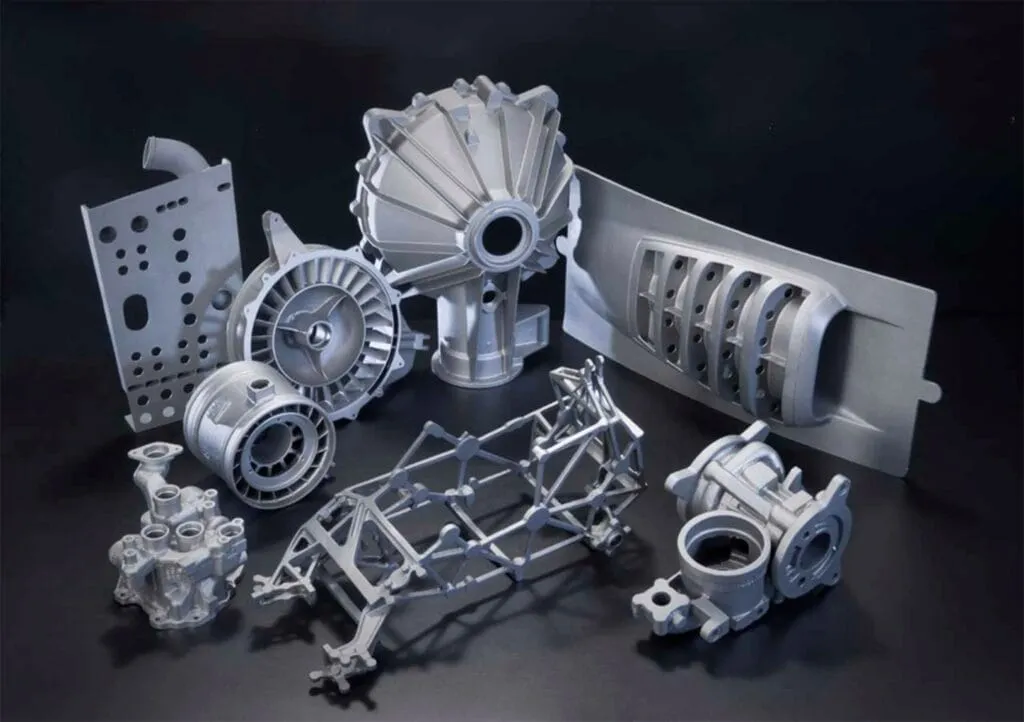
Applications of advanced techniques, including 3D printing tooling & fixtures, are reshaping the automotive sector through design and prototyping in addition to production and other uses. This has made a radical change in conceiving, validating, and building up the vehicles due to the geometries and on-demand part fabrication capability. For engineers, 3D printing in automotive industry frees design constraints and accelerates development through fast iteration.
Meanwhile, manufacturers gain efficiencies in assembly planning and inventory management by 3D printing tools, jigs and specialized components. As materials and technologies advance, more end-use vehicle components are being additively manufactured. Automakers are also leveraging 3D printing in automotive industry to produce ultra-lightweight prototypes and conceptual vehicles. Going forward, the continued maturation of additive techniques will blur production lines, customize experiences and optimize performance metrics like reduced emissions. 3D printing promises to not only enhance individual aspects of automotive engineering but revolutionize the very fabric of the industry itself.
3D Printing Technology in Vehicles
Complex Part Designs with 3D Printing
3D printing in automotive industry allows automotive engineers to design parts with intricately complex geometries that exceed the limits of conventional production methods. Its layer-by-layer fabrication process enables the creation of optimal internal lattice structures, integrated cooling channels and lightweight assemblies not possible through traditional means. This has helped unlock new frontiers in vehicle design focused on weight savings, efficiency and performance.
Additive Manufacturing for Prototyping
3D printing advanced the concept of prototyping since it began, it ease the process which was difficult to master through casting or through CNC machining among others.. Additive processes produce accurate prototypes and proof-of-concept models in hours versus weeks, allowing continuous part refinement. The ability to rapidly print, test and iterate multiple design iterations fosters innovation and speeds new vehicles to market.
On Demand Production of Spare Parts
Rather than holding large part inventories, 3D printing in automotive industry permits the on-demand fabrication of specialized components. Dealerships and repair shops can now access an extensive digital portfolio and print precise replacements for outdated fittings or hard-to-find legacy components. This helps reduce costs associated with storage and obsolete stock, while satisfying niche and custom repair requests.
Overall, guide to 3D printing is enhancing how vehicles are conceived, validated and serviced through complex part possibilities, expedited prototyping cycles and an on-demand approach geared toward optimization, personalized experiences and independent maintenance solutions.
Lightweight Materials for Cars

Weight Reduction through Design Optimization
By 3D printing in automotive industry lightweight yet durable materials, automotive engineers gain more freedom to sculpt vehicles optimized for mass efficiency. Complex geometries with interior hollows or exterior lattices shed kilograms through strategic placement of just the needed material. Every removed pound translates directly to improved efficiency, acceleration, braking and overall performance.
Carbon Fiber Components for Electric Vehicles
Electric powertrains demand strong yet ultra-light housings, panels and internals to maximize cargo volume without sacrificing range. 3D printing in advancing medical carbon fiber composites are increasingly used for high-stress load bearing components, battery enclosures and streamlined body panels requiring rigidity with minimum mass.
Metal 3D Printing of Structural Parts
Aluminum, magnesium, titanium and copper alloys are being additively fabricated for structural elements such as control arms, suspension members and drive shafts. By printing metals with complex lattice-infused geometries, 3D printing in automotive industry manufacturing achieves weight parity with cast/machined originals using 30-50% less raw material through highly optimized internals.
Overall, 3D printing enables mass customization of vehicles through precise material placement. Automakers utilize its design freedom to iterate lightweighting solutions that enhance performance metrics while satisfying evolving sustainability priorities around reduced energy consumption and emissions from mobility solutions.
Automotive Design with 3D printing

Customization of Interior and Exterior Parts
3D printing in automotive industry supports on-demand personalization of interiors and exteriors. Customers can select bespoke color schemes, integrated gadgets, and specialized fittings like ergonomic control knobs or doorsills stamped with logos. Exteriors may sport adornments like optional badges, license plate frames or access panels printed on-demand with team logos.
Sustainable Production through Waste Reduction
Additive practices such as binder jetting eliminate machining scrap by fusing powdered material only where needed. Digital architectures optimize mass placement to construct viable parts while minimizing raw input. Sustainable practices lower environmental impact and appeal to eco-conscious buyers.
Advanced Manufacturing for Unique Vehicles
3D printing facilitates low volume niche concepts unattainable through mass production. Local Motors demonstrated this through the Strait, an Italian high-performance electric model with 3D printing in rototyping body, cockpit and suspension links. As technologies mature, unique vehicles will push boundaries for performance, sustainability and personalized mobility.
By 3D printing in automotive industry production-ready end-use components, automotive designers gain unprecedented freedom over ornamentation, sustainability targets, and pioneering niche designs. The technology cultivates mass excitement around a new era of widely customized and eco-friendly mobility solutions.
Future of 3D Printing in Cars
Mass Production Applications and Materials
Advancing metal and composite 3D printing technology will introduce the technology into high-volume automotive manufacturing. Complex structural parts, fittings and tooling will be additively fabricated, streamlining both production and supply chains. Novel thermoplastics will enable lightweight electrical components
Integrated End-to-End Supply Chain
Centralized digital part catalogs will facilitate true on-demand manufacturing. Dealerships will maintain basic servicing tools while complex replacements are printed locally on an as-needed basis. Outsourced tiers will incorporate additive capacity for optimizing just-in-time workflows.
Evolution of the Automotive Industry
Mass customization possibilities will intensify as 3D printing in automotive industry becomes pervasive. Vehicles may undergo component refreshes to satisfy regulation or integrate new options. Model year cycles will diminish. Independent workshops will thrive through distributed production. Fleets will optimize uptime through predictive part replacements.
As automation proliferates, 3D printing materials will optimize human-machine collaboration. Production innovations will sustain responsible industry practices. Customers will progress from passive observers to design collaborators. Groundbreaking mobility will emerge through integrated additive and computational thinking. The future remains wide open as 3D printing transforms every facet of vehicle engineering, manufacturing and experiences.
Rapid Prototyping in Automotive

Streamlined Design Validation
3D printing in automotive industry accelerates prototyping workflows by producing accurate models directly from CAD files. Engineers evaluate fit, form and function of complex parts that previously required costly long-lead tooling. Multiple iterations can be printed overnight instead of weeks, enabling rapid validation of new designs before tooling commitment.
Faster Iterative Development Cycles
Additive processes minimize the time between concept and test. Design flaws are caught much earlier as interlocking parts, sub-assemblies and entire vehicles can be printed and functionally tested together. Engineers identify failure points or ergonomic issues and refine components in parallel, compressing development schedules.
Cross-Functional Collaboration Tools
Digital market of printable part files enables global collaboration. Remote teams iteratively print, test and provide feedback simultaneously. Prototypes are reviewed through mixed reality tools before tooling begins. Configurations are effortlessly swapped, allowing engineers, managers and specialists worldwide to analyze, discuss and optimize in real-time.
By streamlining validation workflows, 3D printing in automotive industry cultivates an iterative environment that nurtures innovation. Compressing development cycles through rapid testing empowers cross-disciplinary cooperation and quality assurance practices critical to excellence in automotive engineering.
Electric Vehicles and 3D Printing
Lightweight Battery Enclosures
3D printing optimizes battery housings through intricate internal geometries that provide rigidity with minimal mass. Strategically positioned supports absorb impact forces to protect sensitive cells. Complex cooling channels are added without seams for thermal conductivity.
Tailored Drive Components
E-powertrains require specialized elements like motor casings, transmissions and linkages. 3D printing in automotive industry fabricate these high-precision fittings, often out of lightweight metals and composites tailored for electro-mechanical applications. Complex electromagnetic fixtures can also be additively manufactured.
Sustainable Production Methods
Advanced 3D printing fosters sustainability goals in e-mobility. Parts are produced on-demand through efficient material deposition versus energy-intensive mass processes. Renewable thermoplastics offer recyclable alternatives, while waste is minimized through digital architectures. Future innovations will integrate renewable and recycled feedstock..
As the automotive industry transitions to electrification, 3D printing in automotive industry plays an important role in improving performance metrics like range through meticulously manufactured light weighting solutions, bespoke components and sustainable manufacturing techniques optimized for evolving drivetrain technologies.
Automotive Production Innovations
Just-in-Time Manufacturing
3D printing facilitates optimized Just-in-Time workflows. Specialized tools, fixtures and replacement parts are printed on assembly lines per work orders. Manufacturers avoid surplus stockpiles while gaining flexibility to address periodic spikes or variations.
On-Demand Local Production
Dealerships gain the ability to print low-volume or customized additions onsite. Special service components can be produced instantly rather than warehoused. Independent shops flourish through distributed digital catalogs and 3D printing in automotive industry of hard-to-find legacy parts.
Technician Training Applications
Service schools leverage 3D printing to teach complex repair methods. Trainees benefit hands-on by printing non-destructive training modules mimicking real components. Comprehension is enhanced through dynamic access to interactive virtual and physical part replicas optimized for collaborative learning.
Overall, 3D printing in automotive industry transforms production practices through on-site microfactories, optimized inventory levels and immersive educational tools. The technology nurtures efficiency, independent maintenance and continuous workforce development vital to sustain excellence across automotive manufacturing operations.
Conclusion

In conclusion, 3D printing has emerged as the new frontier of technology in the automotive industry that is seen to offer numerous new applications in almost all the areas of the automotive manufacturing process. Designers have the liberty of achieving complex shapes and sizes together with lightweight and strength which have opened new possibilities in the field of engineering.
Likewise, on the manufacturing side, different value-chain partners are getting more value by experiencing reduced costing and time through innovations such as rapid prototyping, on-demand manufacturing, and local production. As the materials and the technologies of 3D printing in automotive industry are improving, additive processes are to remain among the most perspective for the point of high-velocity car production and the supply chains with their integration.
Another aspect of sustainability goals is also achieved through material intensity and electric vehicles solutions that stem from 3D printing technology. In the future, its implementation will define the individual approach to the customer and change the practices of the industries of mass customization, mobility, and creating the necessary tools for personnel training. The future of automotive engineering is one of constant progress, as enhanced by 3D printing in automotive industry, which opens the door to further development of integrated design processes and efficient production and sustainable mobility for the emerging autonomous vehicles.
FAQs
Q: What are then the main advantages of using the 3D printing in automotive design?
A: It is used in creation of geometries, in changing prototypes frequently and in creating different customizations of parts at once.
Q: How can 3D printing help reduce vehicle weight?
A: Through design optimization with strategically placed infill structures and use of lightweight metals like aluminum and titanium.
Q: Which electric vehicle components are being 3D printed?
A: Battery housings, motor parts, transmissions and specialized linkages require precision manufacturing suited for 3D printing.
Q: What production applications is 3D printing improving?
A: Just-in-time manufacturing through on-demand parts, reduced warehousing needs, and localized repair shops printing hard-to-find components.
Q: How can 3D printing enhance the workforce?
A: Immersive training modules replicating complex systems can be printed for hands-on technician education.