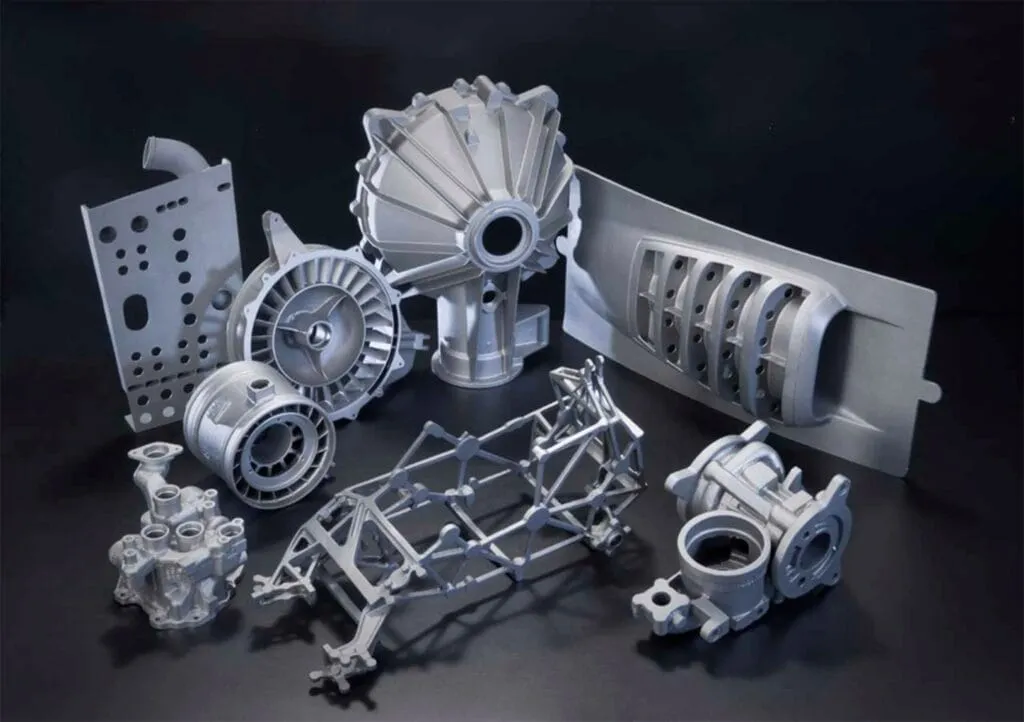
This element in metal 3D printing calls for stronger and more complicated part shapes that are light in construction and were previously unachievable. Find out how different industries are transforming their titanium, steel, and aluminum components into printed parts. It is this state-of-the-art solution that addresses constraints to change the way products can be designed and assembled.
How Metal 3D Printing is Transforming Everything

You gotta check out this crazy new way of making stuff called 3D printing. Scientists came up with a technique where you can build objects by stacking tiny pieces together layer by layer. Most 3D printers use plastic, but now there are special high-tech machines that use metal too!
Metal 3D printing is allowing engineers and designers to totally level up their creations. They can produce parts that are super strong yet lightweight at the same time, all because of how the layers of metal fit together. This tech is revolutionizing industries like aerospace, cars, and more. Now we can construct things that weren’t possible before.
The process that we use in metal metal 3D printing is called powder bed fusion. They sprinkle a thin coating of metal particles onto a platform. Then a mega powerful laser comes in and heats up specific spots of the powder based on the blueprint. This fuses the powder together to make a solid sheet. The platform lowers a little and they add another powder layer. The laser melts that one onto the first. Layer by layer an entire object forms out of melted metal grains!
What’s so amazing about using metal versus plastic? Metals like steel and titanium are way tougher and can withstand higher temperatures than plastics. Metal parts will last through way more wear and tear. This futuristic printing is enabling creations stronger than ever before. The possibilities are endless! Things made with metal last a really long time. Metal parts are also good for electronics because metal conducts electricity.
Another awesome thing is that you can 3D print very complex shapes with metal that would be nearly impossible with traditional manufacturing methods. Designers can make objects with complicated inside parts, moving pieces, and even create lightweight “skeleton” structures inside using the space inside objects better. All sorts of new designs are now possible that give products better performance.
In conclusion, metal 3D printing is revolutionizing how things are made. It allows for stronger, longer lasting products with shapes and designs never seen before. This technology will help create all kinds of innovations in many industries for years to come!
Choosing the Right Metal

Using metal as a substrate in printing has proven to be a better proposition for engineers and designers because it offers the opportunity to select the right type of metal for a part. There is specific reason why different metal alloys are suitable for particular applications; they differ in several aspects.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a versatile material used in the Metal 3D Printing because it is very hard wearing. It is strong and does not easily corrode by water or any other chemicals which affect its metallic nature. That is why it is desirable for the material of creating objects that are to last a long time in harsh conditions – tools, industrial parts, etc.This makes stainless steel great for objects that need to last a long time in tough environments, like tools or industrial parts. However, stainless steel is denser than some other metals so parts made from it can be heavier.
Aluminum
A specific feature of such materials is their lightweight and relatively high mechanical properties, which allow their use in many industries. That makes aluminum ideal to be used when there is need to compromise on its weight for instance for use in aircraft and electronics parts. Aluminum metal 3D printing at a fast speed and is not as hard to further work on the material post 3D print. It cannot however be used for highly heated applications as it is with other metals.
Titanium
Titanium is far stronger than steel and yet it incorporates almost half the amount of density as steel does. It is especially suitable for any situation in which strength and stability combined with low weight is needed, such as in surgeries or aerospace projects. But when an object is to be 3D printed with titanium it would be relatively costly as it is a hard material and needs special printers to work with.
The Future of Multi-material Printing
New advancements allow 3D printers to simultaneously use two or more different materials in one print. This “multilateral” printing opens up possibilities like making parts with customized exterior textures or internal frameworks of varying metals. In the future, 3D prints could have complex material properties optimized for many applications. Engineers will continue developing new metal alloys optimized for metal 3D printing technology.
Overcoming Obstacles to Advance the Technology

3D printer cost with metals allows designers to create amazing things. However, metal 3D printing still has some challenges to overcome.
We need very high temperatures to melt the metals like steel and titanium. Specialized laser systems with precise control are needed to heat metal powder just the right amount without damaging the material. Building parts layer by layer also causes shrinkage and internal stresses as layers cool.
After printing, some metal parts need “post-processing” treatments to make them even stronger. Heat treatment helps relieve stresses in the material from the printing process. Machining smooths surfaces and shapes parts to their final form. These extra steps add time and cost to production.
Figuring out solutions to these obstacles drives further innovation in 3D printing technology. Engineers are developing new metals especially for 3D printing that melt at lower temperatures but still perform well. Advances in control systems deliver laser power even more accurately. New post-processing methods speed up the hardening process.
Metal 3D printing faces hurdles like heating challenges and stresses within parts, the technology has revolutionized design and made production easier. As scientists find ways around these obstacles, industries will unlock even more potential uses for 3D printed metal components. Future breakthroughs promise to transform how products are engineered and manufactured in amazing ways. The possibilities seem endless as innovation continues!
Conclusion

In closing, metal 3D printing has brought about an industrial revolution that is transforming design and manufacturing. This advanced technology allows products to be engineered with incredibly complex geometries and lightweight structures that were never before possible. When we use metals such as steel, aluminum and titanium facilitates production of rigid and durable parts for rigorous tasks. Although the technical issues of high melting points and internal stressing, which are crucial in this application, are still unresolved, innovations are growing exponentially to solve it.
With these developments steadily growing and improving, integrated metal 3D printing will open up a world of possibilities in applications ranging from aviation and other industries, to biomedical. This technology will enable designs, materials and applications that can drive unending innovation and keep the revolution alive for many more years. Obviously, Metal 3D printing is moving the genus of what can be produced to a whole new level.
FAQs
Q: Is metal 3D printing expensive?
A: Metal 3D printers and metal powders can be costly. However, it reduces wasted materials and enables low-volume production which reduces costs compared to traditional manufacturing.
Q: In what sorts of metals 3D printing is possible?
A: Specific metals used in the fabrication practices include steel, aluminum, titanium and nickel products. It is also important to understand that gold and silver are not an exception to 3D printing.
Q: How do you 3D print with metal?
A: A laser selectively fuses metal powder laid down in thin layers. The part is built up layer by layer. Post-processing may be needed to improve properties.
Q: What industries use 3D-printed metal?
A: Aerospace, automotive, medical and dental are major sectors. Other growing uses include electronics, oil/gas, consumer goods and more.