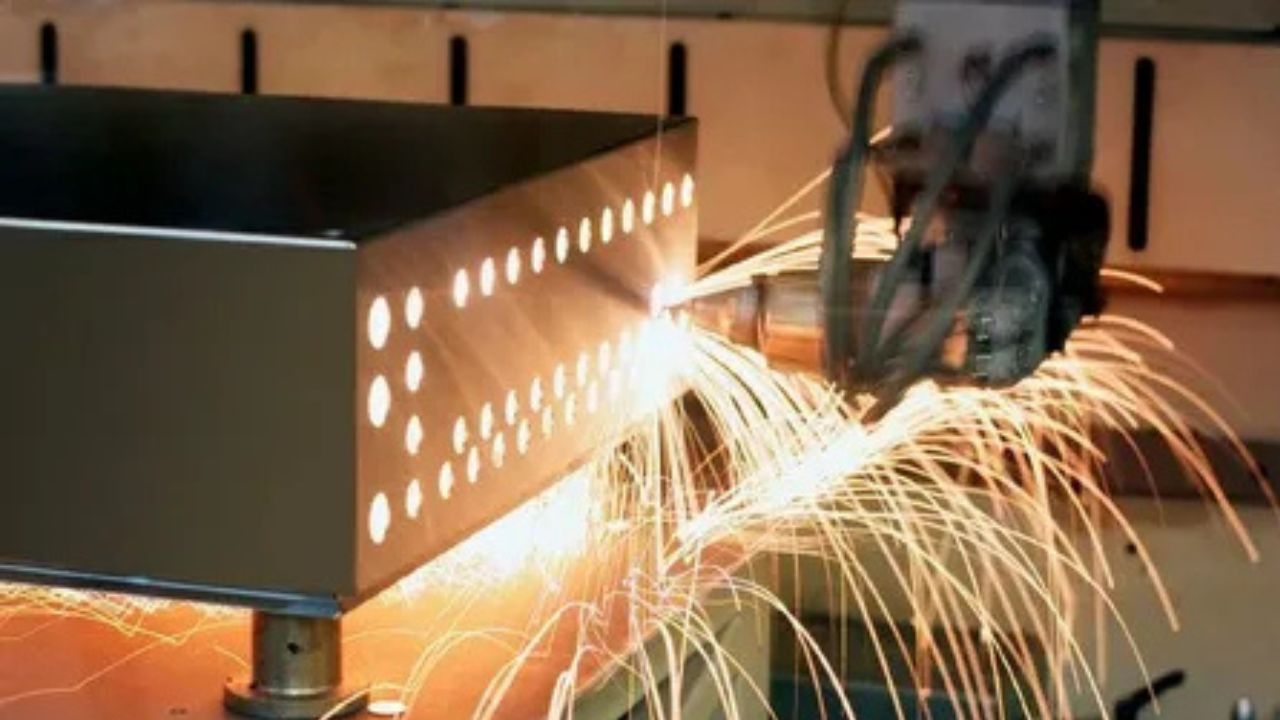
CNC (computer numerical control) machining is the use of tools targeting materials and trying to cut them with the guidance of a computer. This article discusses the most general CNC Machining processes as milling and turning, the type of material that can be machined, the level of precision possible, and the industries that use CNC including aerospace, automotive, and medical industries.
CNC Wizardry: Crafting Metal with Computer Control

Have you ever seen machines that can shape metal and plastic all by themselves? They are called CNC machines. CNC stands for computer numerical control. These machines use computer programs to shape materials very precisely into all sorts of useful things.
One type of CNC machine is called a milling machine. It has spinning drill bits and end mills that can cut away at blocks of material. Engineers design 3D models on computers and the milling machine follows those plans to carve out the final shape. The mills can spin in all kinds of directions – side to side, back and forth, up and down – to make complex designs. Sometimes mills even have 5 directions of spinning! They leave behind exactly what the computer tells them to.
Another machine is called a lathe. On a lathe, long cylinders of plastic or metal get spun very fast. As it spins, cutting tools shape the outside of the cylinder. Lathes can create circles, spirals, and all sorts of curves on the outside edges. They can also dig tools inside the spinning cylinder to make holes and intricate patterns. Engineers use lathe machines to make things like bottles, pipes, rods and more.
Besides milling and turning, there are some other useful CNC techniques. One is grinding, which uses grinding wheels instead of drills and mills to shape parts. Another is EDM, which uses electric sparks to precisely melt away tiny bits of material without ever touching it! Some CNC machines can even put smooth, shiny finishes on parts after they are done cutting.
All these computer-guided machining methods allow people to create very complex and accurate designs. Anything you can imagine on a computer can be made into a real physical object with CNC. Whether it’s parts for cars, planes, phones or countless other products, CNC machines make modern technology possible. The computers precisely control the machines to cut perfect replicas of virtual 3D models. Pretty cool, huh? CNC is how we turn ideas into real things!
Tolerancing for Precision Parts
Most CNC shops follow ISO 2768 rules for how precisely parts need to be made. This standard outlines tolerances for sizes of different features. For example, holes might only need to be within 0.1mm of the planned size. Parts can be made even tighter than the standard if a customer needs super accuracy.
Small Sizes and Close Measurements
CNC machines can shape materials down to very small scales. Hole sizes, walls, and other part details as small as 1mm can be cut very precisely. Machinists can also control location of features within tight tolerances, like being no more than 0.01mm off where drawings say they belong. This allows complex, tiny internal and external structures to be replicated again and again to tight tolerances. So from macro to micro dimensions, CNC excels at precision manufacturing!
Choosing the Right Material
Working with Metals
CNC machines can shape lots of different metal materials. Aluminum is lightweight and easy to work with. Steel is very strong. Stainless steel doesn’t rust. Copper and brass have a nice look. Titanium is super light and tough. Machinists pick the best metal for each job.
Working with Plastics Tool
CNCs aren’t just for metals – they can cut plastics really well too. Plastics like nylon and PVC are used to make all sorts of products. polyoxymethylene (POM) is very hard and stiff. PTFE is slick like Teflon. Using plastics lets designers be creative and companies make products faster.
Finishing Touches
After CNC cutting, parts often get an extra treatment to protect or enhance them. Sandblasting makes surfaces rough. Anodizing makes aluminum colorful. Electroplating puts on metallic coatings. Powder coating bakes on durable paint. Polishing creates a shiny look.
Custom Finishes
The right surface finish depends on the product. Some need to resist rust or chemicals. Others call for special textures. Designers work with finishers to get just the right coating, color or shine for each application. The finish is the final touch that makes a part perfect for its job.
Making Sure Parts Come Out Perfect

CNC machines can make things very precisely, but people still need to double check the work. That’s where quality control steps in. The finished parts are carefully inspected. Machinists use measuring tools like micrometers and calipers to check sizes and distances between features. If anything is too big or small, too close or far, they find and fix problems. This way, all the pieces stay within the tolerance, or acceptable range, set by the engineers and customers. The inspections guarantee customers receive products made exactly as ordered.
All the Tools required to Get the Job Done Right
This factory has a huge collection of CNC machines to handle just about any project. Over 100 mills and lathes can remove material in 1 to 5 different axes. Having so many different machines means any geometry can be made, no matter how complicated.
Precision and Pace
The CNCs here can shape parts within thousandths of a millimeter! That’s smaller than a sharp needle. Plus quick changeover between jobs means fast lead times, often just days for prototypes or one-offs. Customers don’t have to wait long or settle for less accuracy.
Whether a simple shape or intricately engineered component, the perfect process and material are available. Design software links to machines for efficient production from drawings to finished products. Engineers help clients transform concepts into high-quality, mass-producible objects. Together advanced technologies cut time and costs while ensuring precise specifications – that’s what lets this place tackle any manufacturing need!
Many Fields Benefit from Computer-Guided Crafting

Cars Get a CNC Boost
Automakers need strong, lightweight parts in huge numbers. CNC delivers the answer with its prowess for mass-producing consistent complex shapes. Steering gears, engine blocks and more flexibly roll off highly programmed automated machines.
Precision is Planes’ Priority
For aerospace the smallest deviations are unacceptable risks. CNC’s repeatable micron-level resolution reassures in component manufacturing. Wings, fasteners and critical hardware undergo careful CNC formulation for optimum strength and safety in flight.
Whether a simple shaping or intricate geometric network, diverse industrial sectors now employ CNC to increase quality output. Another vital user is medicine: here computer-conducted machining fabricates replacement joints, surgical tools and aids medical discovery with tailored prototyping. Overall computer managed modeling multiplies what manufacturing can achieve – benefitting not only product development but technological progress overall.
Conclusión

In summary, Mecanizado CNC has revolutionized modern manufacturing by providing a fast, flexible and highly precise way to shape all types of materials. Whether removing material millimeter by millimeter or sculpting microscopic structures, CNC multi-axis machines precisely replicate digital CAD models thanks to numerical computer control.
A wide assortment of CNC tools from lathes to grinders expand what designs can be realized in anything from aluminum to plastics. Likewise, surface treatments broaden applications by providing protection, aesthetic finishes or specialized properties. Quality assurance techniques coupled with production speed and complexity have made CNC indispensable across numerous industries. Computer numerical control continues advancing what is possible through precision crafting. In the future, ever-more sophisticated CNC technologies will further transform design and fabrication.
Preguntas frecuentes
Q: What types of materials can CNC machines cut?
CNC tools can shape metals like aluminum and steel as well as plastics, composites, and other materials. Popular choices are metals for strength and plastics for their design flexibility.
Q: How small of features can CNC machines produce?
Very high-precision CNC tools can cut microscale textures and holes as small as 1-2mm. Intricate designs with fine details and tight tolerances are within their abilities.
Q: How quickly can CNC machines produce parts?
Production speed depends on part complexity and machine availability. However, CNC facilitators can often turn around prototypes within days and larger volume jobs within a couple weeks once the machining program is setup. Quick turnarounds make CNC very suitable for iterative design processes.


