CAD/CAM programming and CNC machining are at the forefront of modern product development, transforming the way products are designed and manufactured. With model-based definition, on-demand production, and mass customization, these technologies streamline workflows and deliver unparalleled precision and efficiency. This article explores how CAD/CAM and CNC machining are revolutionizing product development, from prototyping to precision manufacturing.
From Bits to Atoms: CNC Machining in the Digital Age

This article begins with an introduction that provides an overview of how advanced innovation is transforming product development. It then delves into CAD/CAM programming, covering model-based definition and CNC programming. Next, it explores multi-axis machining, highlighting increased levels of freedom and the capabilities for complex prototyping. The discussion continues with advanced manufacturing, focusing on on-demand production and mass customization. Following that, the section on prototype development examines the role of CNC machining in enabling rapid prototyping. The article also addresses precision tolerances, detailing advances in CNC machining accuracy. Finally, it concludes with insights on the future of product development in the digital manufacturing era and includes a section of FAQs that answers key questions about CAD/CAM and CNC machining.
The insurgency of advanced innovation has changed how items are planned and created. Progresses in computer aided design/CAM programming and CNC (PC Numeric Control) machining have empowered originators and specialists to imagine and prototype items in phenomenal ways. This article investigates how key patterns in computerized assembling, for example, multi-axis machining and model-based definition are smoothing out the item development process.
CAD/CAM Software: The Backbone of Digital Manufacturing

Model-based Definition
Computer aided design programming permits fashioners to make 3D models of parts and congregations in a virtual climate. With model-based definition, all applicable part and gathering data including math, tolerances, materials and completions can be implanted in the 3D model. This disposes of transitional paper-based drawings and empowers producers to straightforwardly import computer aided design information for CNC programming and assessment.
CNC Programming
Computer aided design models can be moved to CAM (PC supported assembling) programming for the age of machining ways and G-code programs. Contrasted with physically programming machines, CAM programming mechanizes this interaction and lessens mistakes. It permits complex calculations to be machined effectively utilizing multi-axis CNC machines. Include based programming maps computer aided design model highlights to assembling activities.
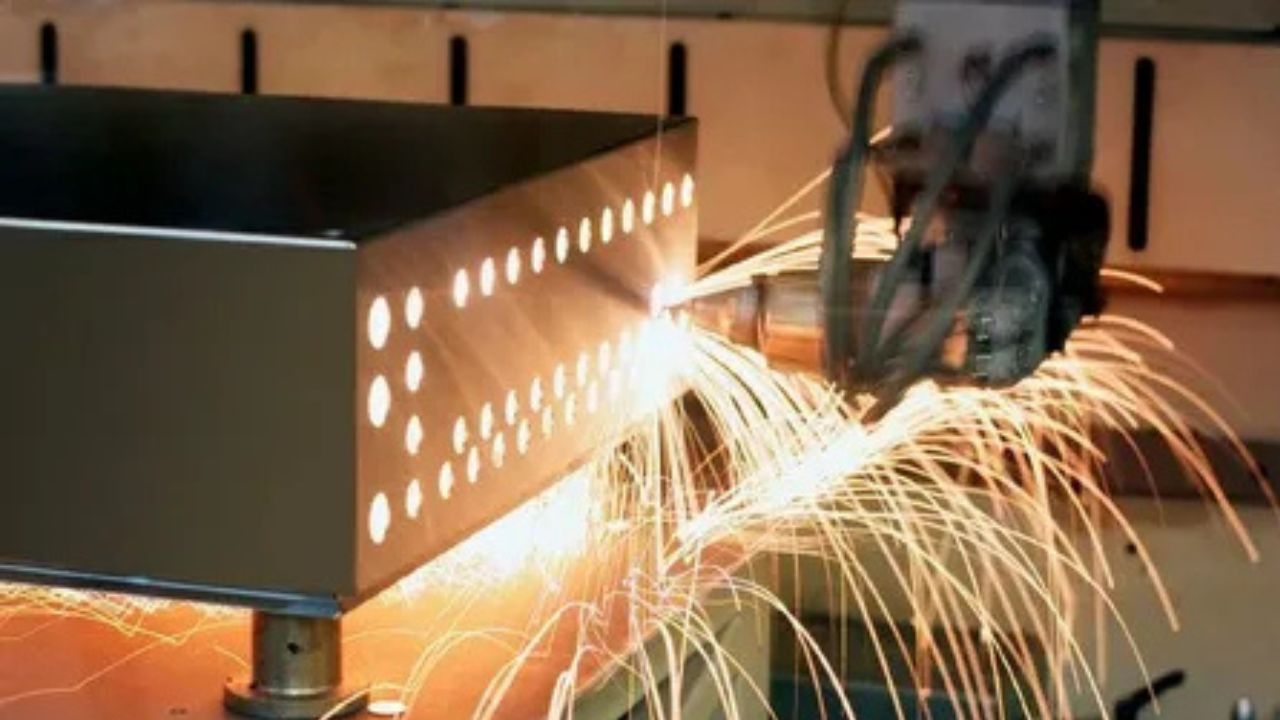
Multi-axis Machining
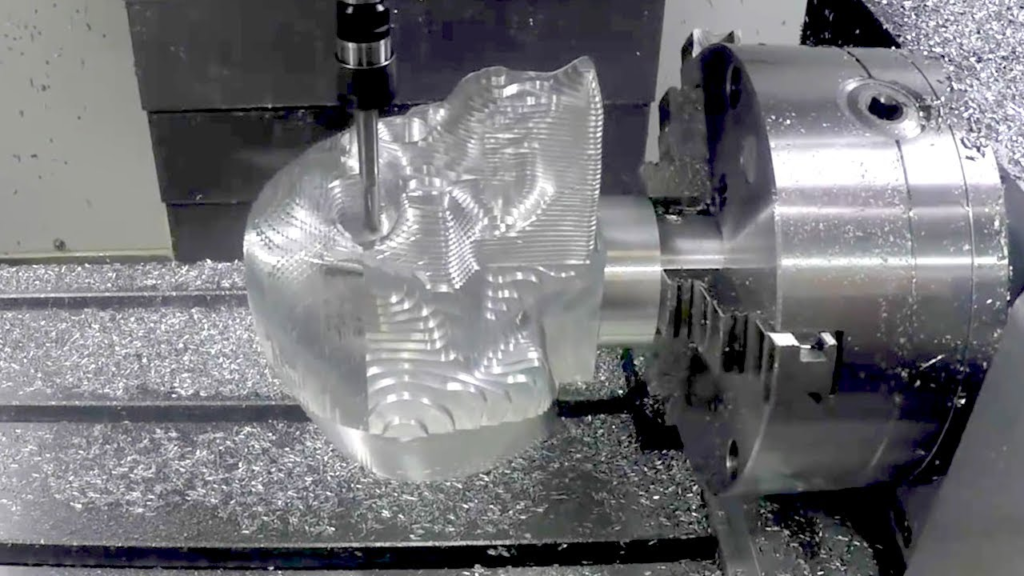
Increased Degrees of Freedom
Conventional 3-axis CNC machines move the toolhead along the X, Y and Z tomahawks. Extra rotating tomahawks empower non-linear profiles to be machined with a solitary set-up. 4-and 5-axis machining gives more levels of opportunity to complex surfaces. It dispenses with the requirement for re-fixturing parts between activities, lessening arrangement times and further developing precision.
Complex Prototyping
With multi-axis capacities, profoundly complex molds, passes on and prototype parts can be machined straightforwardly from PC models with insignificant manual wrapping up. This abbreviates lead times versus conventional subtractive strategies including multiple arrangements. Complex calculations that recently required broad hand-creating or projecting can now be cut with a solitary program.
Digital manufacturing
On-request Creation
Advancing Impresión en 3D y Mecanizado CNC innovations have empowered conveyed, on-request fabricating abilities. Online stages interface creators with makers so computerized plans can be transformed into actual items locally when and where they are required. This diminishes warehousing expenses and lead times contrasted with customary bunch creation techniques.
Mass Customization
Computerized manufacture enables mass customization by permitting items to be customized for an enormous scope. Boundaries like tones, materials and mathematical elements can be altered per request. When joined with mechanization, on-request fabricating is reasonable for both high-volume creation and low-volume series of particularly customized items.
Prototype Development
CNC machining speeds up the prototype development process by empowering quick emphasess. Plans can be demonstrated rapidly through completely utilitarian prototypes preceding focusing on additional costly apparatuses and creation runs. Tight creation tolerances guarantee prototypes intently match the planned plan purpose. Quick CNC machining abbreviates the item development cycle, permitting new items to arrive at market quicker through a productive approve learn input circle.
Precision Tolerances
Propels in CAM programming, CNC controls and machining focuses have fundamentally further developed precision tolerances achievable through CNC machining. More tight tolerances moving toward those of infusion shaping are empowering complex metallic parts to be prototyped or even efficiently manufactured involving CNC with diminished need for post-process wrapping up
Conclusión

The intermingling of advanced innovations like computer aided design/CAM programming, Mecanizado CNC and added substance fabricating is upsetting the way in which items are planned and produced. It has empowered a shift towards disseminated, on-request creation models that smooth out processes from plan to manufacture. Multi-axis CNC specifically has extended what calculations can be exactly machined, taking into consideration profoundly complex parts and tooling. When joined with robotization it works with savvy mass customization at scale. As machining capacities keep on progressing, CNC is progressively turning into an essential creation strategy, from prototyping through mid-volume runs. The synergies between these advanced innovations will additionally upgrade item development work processes, meeting mechanical and market needs quicker through more productive approval, learning and constant improvement cycles.
Preguntas frecuentes:
Q: What are the fundamental benefits of computer aided design/CAM programming?
- Model-based definition streamlines producing by wiping out transitional drawings.
- Robotized CNC programming diminishes mistakes and streamlines toolpaths.
- Complex calculation can be machined with a solitary installation arrangement.
Q: What sorts of elements can multi-axis CNC machines produce?
- Non-linear profiles through extra rotational tomahawks past the common 3 linear tomahawks.
- Profoundly unpredictable pockets, holes and etched surfaces through 5-axis concurrent or 5+2 axis consecutive machining.
Q: How has advanced assembling affected creation models?
- On-request disseminated fabricating brings down costs by creating locally when and where items are required.
- Mass customization at scale permits items to be custom-made per client by means of computerization.
Q: What items are appropriate for CNC machining?
- Prototypes across ventures for structure and practical approval preceding creation.
- Molds, bites the dust and apparatuses for assembling different products.
- Precision aviation, clinical and hardware parts.
Q: How do machining tolerances contrast with different cycles?
A: While not exactly as close as infusion forming, CNC tolerances have improved essentially and are moving toward those of other subtractive techniques like processing without posts-process work.


